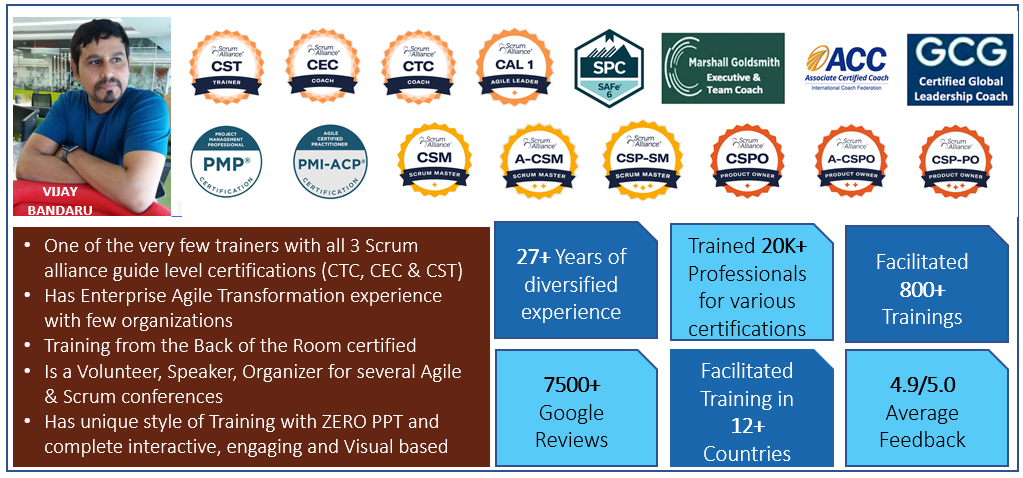
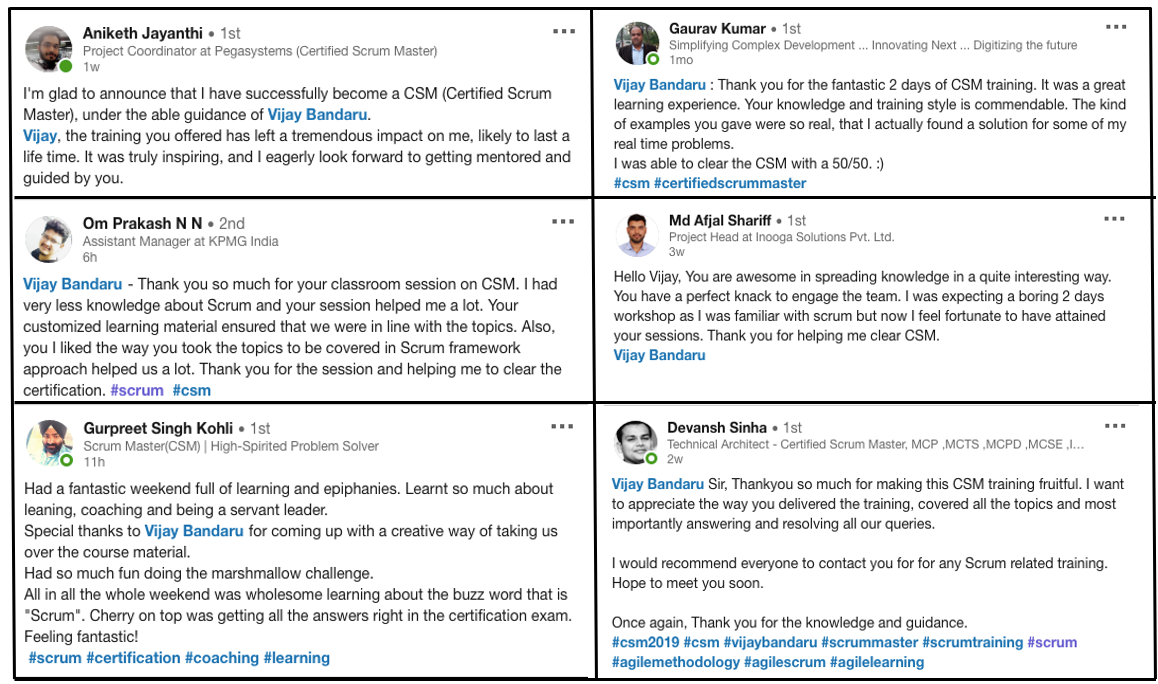
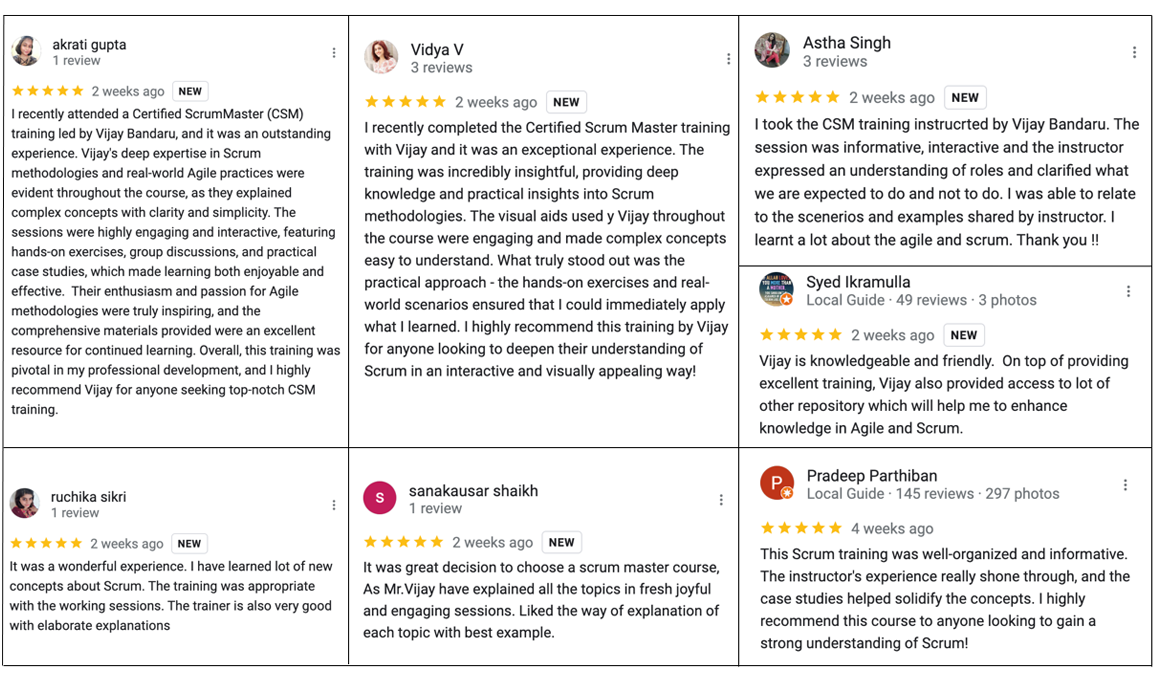
Our Training (classroom or live virtual) are based on brain based learning approach and techniques. We understand “knowledge is precious” so we create it with responsibility. We use limited class size with personal attention, interactive learning, activity based understanding of concepts, simulations and group discussion with knowledge sharing. So overall, it will be a fun filled, thought provoking learning experience for you. Below will be brief agenda of the topics that you will understand in the CSM (Certified Scrum Master) workshop.
Workshop Setup:
I use Scrum to teach Scrum. So I will introduce key elements of Scrum and we create a Vision for the workshop based on your objectives. Then we will agree on a backlog for the Training. As a Trainer, I will own and manage the Training backlog. We will agree for a Definition of done for the class and a Sprint duration. Typically the two days Training will be divided into 4 half-day Sprints. We will do a Sprint Planning for the 1st Sprint and the participants will create a Sprint Burndown to track the progress. I will create a Release Burnup to track overall progress of the class. Then we will begin each topic discussion.
Agile introduction
Here we explore what is Agile, why Agile and how Agile helps organization. We also learn the 4 pillars of Agile. We discuss this taking an example and drive the conversation. We also do an activity called “Value vs waste”. We also deep dive into the “Growth Path” stages and how organizations get into resistance through Agile Transformation and how to deal with that.
Agile Manifesto
In this topic, we will understand the 4 values and 12 principles of Agile Manifesto. We cover how these values and principles help individuals and teams in Organizations to become Agile. We also discuss some challenges involved in implementing these values and principles and understand the possible solutions.
Process Controls
In this topic, we deep dive into understand Simple and Complex problem domains and how simple problems can be tackled using “Defined” process and why complex problems cannot be tackled with a “Defined” process. We understand the “Empirical” Process to address complex problems. We also discuss several examples from real-world to understand the difference between the Defined and Empirical Process controls.
Scrum Overview
We will understand the high level overview of Scrum Framework elements and the flow. Scrum has 5 Values, 3 Accountabilities, 3 Artifacts, 5 Events and 1 Activity. We will understand the purpose of these elements and what happens if they are used in wrong way.
We will also discuss why Scrum is a Framework, not a Process or Methodology or Technique. We also discuss why Scrum is Simple but not Easy.
We also take an example “online portal for recruitment management” to understand the Scrum framework flow. This example helps you to understand right from creating Product Backlog, Sprint planning, Sprint Goal, Sprint Backlog, how the selected items will be implemented, Definition of Done, Product Backlog Refinement, Product Increment, Sprint Review and Sprint Retrospective. As you go through an example by seeing the flow, it makes it more impactful learning.
Scrum Values
Scrum has 5 Values. Easy to remember “FORCC”: Focus, Openness, Respect, Courage, Commitment. We deep dive why these values are important for Scrum Team and Organization, what happens if these values are not followed and how Scrum Master can help injecting these values into the DNA of the teams. How these values will help teams to become high performance teams also will be discussed.
Sprint
We will deep dive into what is Sprint, what is the duration of a Sprint in Scrum, why it is timeboxed, what are the events within a Sprint, who defines the Sprint duration, What is the role of the Scrum Master in Sprint duration decision. We also understand what is Sprint Cancellation, reasons for that, who is authorised to make a call on Sprint Cancellation. Finally we will have a recap activity in which you will understand inter Sprint water fall, intra Sprint waterfall and actual Scrum.
Scrum Team
The three key Accountabilities in the scrum team are the product owner, Developers and the scrum master. These roles will have a Purpose for existence, a Set of Rights and a set of Responsibilities. We will deep dive to understand all these three roles in the Second Sprint.
- Product Owner Accountabilities – The person who is responsible for prioritizing the work and one who owns the ROI of the project is called the product owner. This person understands the customer need and creates the product backlog.
- Developers Accountabilities – The set of people who are involved in writing code and developing the project is called the development team. These people will pull product backlog items and will focus on completing the same.
- ScrumMaster Accountabilities– The scrum process is implemented with the help of the scrum master. This individual bridges gap between the team and the product owner. He/she hears the team view to help them resolve issues to work towards the goal of the company.
Product Backlog
The evidence of human action is called artifact. In the scrum, it is represented in the form of a list, graph, etc. Artifacts are called information radiators. With this radiators, it is possible to achieve transparency in scrum projects which is one of the pillars of the empirical scrum process. Among the many, the three main artifacts are product backlog, sprint backlog, and increments.
Product backlog is one of the 3 artifacts of Scrum. It contains all the items that are needed to develop the Product. They include: Features, Requirements, Infra items, Enhancements, Non functional and defects The product owner owns and manages the Product Backlog. We will deep dive into Product backlog management, characteristics and also you will create a Product Backlog for a simulation Project.
Product Backlog Refinement
The activity involved in understanding, prioritising and estimating the related item before sprint planning is called product backlog refinement. In simple words, the process in which the scrum team decides about the time required to complete each backlog. Based on this estimate they can refine the number of backlogs during each sprint.
Product increment
The increment is the sum of all items that are completed during the Sprint and the value of all the increments of previous Sprints. We will discuss who will create the increment, how do they create, what does it mean by “Potentially Releasable”, who will have the right of releasing the increment to the end users in this topic.
We also discuss about “Technical Debt” and possible reasons for creating technical debt, scrum master role in helping team in addressing the technical debt and what are the consequences of Technical Debt on long run on the Product in this topic.
Agile Estimation (Not part of Scrum)
You will have a lay man understanding of estimation using a simple example of “estimating fruits”. Because it is non-software related, anyone can easily understand the concept. We will have deep dive of relative sizing estimation using “Planning Poker” and we will also discuss release planning and how to track the release progress using “Burnup” chart.
You will estimate the items that you have created in the Product Backlog section and come up with prioritization and release plan for those items.
Definition of Done
In this topic we will understand what is Definition of Done, who creates it, when do they create, what is the importance of Definition of Done, weak Definition of Done and consequences of it, when can Definition of Done be changed. We also discuss how Definition of Done to be created in a multi team project environment.
We will also discuss the difference between Definition of Done and Acceptance Criteria in this section.
Sprint Planning
Sprint planning meeting happens at the beginning of the sprint to discuss the work for the current Sprint. We will discuss who participates in Sprint Planning, what is the timebox, inputs, outputs and how Sprint Planning will be conducted. We will also explore a sample Sprint Planning. We will discuss the differences between Product Backlog and Sprint Backlog. We will also explore the relationship between Sprint Goal and Sprint Backlog and also Product Vision and Sprint Goal.
Sprint Execution
Sprint execution is the next step after the planning is over. The team has mutually agreed to complete the product backlog items selected for the Sprint and hence will start executing them. If the planning is done after discussing, then execution will be on track. In case of any hurdles, these issues will be discussed during the next sprint meeting and the sprint backlog will be executed. How development team works to accomplish the Sprint Goal during the execution will be discussed.
Daily Scrum
In this topic, we will explore the Daily Scrum event. We understand the purpose, participants, timebox and some dysfunctions that usually happen in Organizations with respect to the Daily Scrum and possible solutions. We also explore what is the role of Scrum Master in Daily Scrum, why he/she is optional, how impediments can be raised in Daily Scrum. We will also learn some techniques that help Scrum Master to keep the Daily Scrum within 15 minutes timebox.
Sprint Review
We discuss how Sprint Review is important for the feedback from stakeholders and the participants, timebox and inputs and outputs. We also understand what is the role of Product Owner in Sprint Review in this topic. This is a inspect and adapt opportunity for the Product related improvements.
Sprint Retrospective
We will understand how to conduct the Retrospective, what is the role of Scrum Master in Retrospective, why it is Scrum Team’s private meeting in this topic. We also discuss 4 to 5 techniques to conduct effective retrospectives.
Sprint Burndown and Release Burnup charts (Not part of Scrum)
The sprint burndown chart is used to monitor the progression within the sprint under the following situations. Burndown helps the Development Team to track the work remaining against the time remaining. In order to understand the burndown, the participants will track the class throughout two days in 4 Sprints. It helps participants to understand various situations that might occur in the Scrum Project.
Likewise, the release burnup chart is used to track the progression of the scrum project as a whole. It helps the Product Owner to track progress at the end of every Sprint and can provide better information to Stakeholders.
Simulation
You will do a simulation during the second day of training in which you get a chance to implement the concepts learned during the training. This simulation helps you to visualize and experience how you can lead a Scrum project end to end at your work place.
Recap
At the end you will validate your learning through a powerful activity which tests your knowledge that you have acquired in the 2 day training. This activity also help you to confirm yourself on your readiness for the CSM exam.




 Certified ScrumMaster®
Certified ScrumMaster®
 Certified ScrumMaster®
Certified ScrumMaster®
 Certified ScrumMaster®
Certified ScrumMaster®